In the Playback section we list the common features shared by all player engines (PlayerEngine.apple)
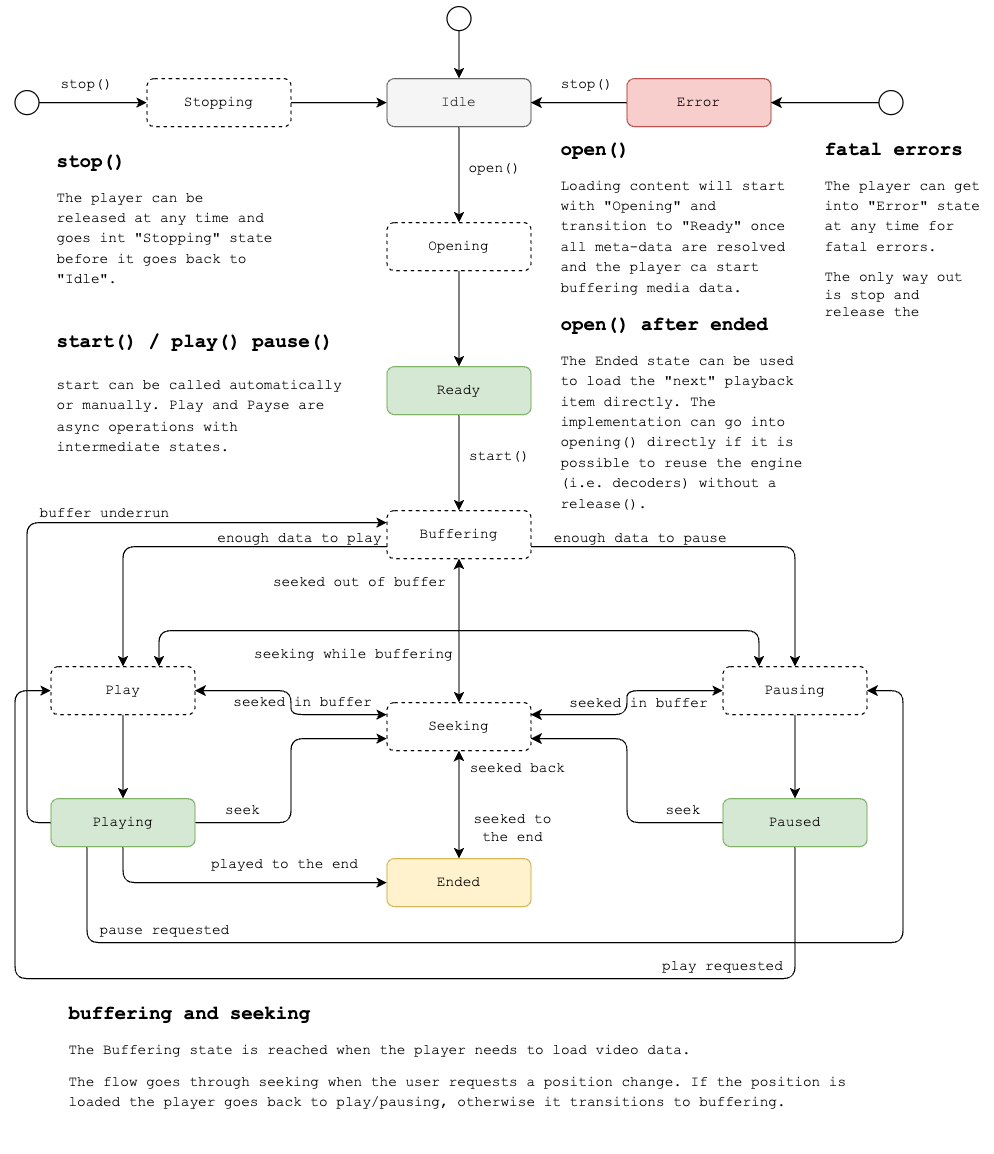
Player states
The following are the possible player states:
Idle The player is in
.idlestate when no content is loaded or being loaded and no additional resources are open. No data is loaded in buffers and no decoder instances are open. This is the initial state of the Player.Buffering: The player does not have enough data to keep in playing and need to fill its buffers further before playback can continue
Ended: The final state of the player is reached when the playhead moves to the end of the available content either by normal playback or via a seek operation that seeks at or beyond the end of the content. The player will stay in the
.endedstate until it is released or the user seeks back into the content timeline. In addition to releasing, the player can also transition toopeninghere. This allows to load new content that re-uses existing resources such as decoder and DRM instances.Error: The player ends up in the
.errorstate after a fatal error occurred. The player can not get out of the Error state itself and needs to be released.Opening: The player is in
openingstate when it started loading content. It will stay in this state until it has enough meta-data loaded to build up a track model and transition to.ready.Paused: Playback is possible but paused.
Pausing: The player is trying to pause playback.
Play: The player tries to start playback. This operation might fail, for instance because if auto-play not being permitted, in which case the player transitions to
.pausing. Usually the player transitions out to.playingand playback starts.Playing: The playhead is moving forward and the content is playing
Ready: The player reached the
.readystate when enough data was loaded to build a track model. At this point how the player proceeds depends on the configuration. The player will in the.readystate until it is transitioned out of the state and loading of data is triggered. This transition can happen automatically or manually depending on the configuration.Seeking: A position change was requested. The player can either reach the new position in its buffer and will transition back to
.playor.pausingdepending on where it came from or it will first transition into.bufferingif the requested position is not found in the current buffer.Stopping: The player is in the process of releasing all its resources (decoders, buffers etc).
The state graph highlights some of the actions that trigger certain transitions. This covers transitions in and out of .idle state and what happens on errors.
Basic playback
An example project of basic HLS playback is provided as part of the PRESTOplay SDK. The example is located in the Examples folder and can be opened with Xcode.
import PRESTOplay
import CastlabsApple
// Initialize the SDK and register the plugins
_ = PRESTOplaySDK.shared.setup("LICENSE", [HLSPlugin()])
// Create the player
var player = PRESTOplaySDK.shared.player()
guard let contentURL = URL(string: "https://example.com/master.m3u8")
else { return }
// Configure the player
let config = PlayerConfiguration(with: contentURL)
player.load(config: config)
player.onState = { previous, state in
// Handle player state changes
switch state {
case .ready:
print("Player ready")
// handle other states ...
}
if let error = state.playerError {
print("Error \(error)")
}
}
// Attach the player to the view
player.attach(to: view.layer)
// Start playback
player.open(autoplay: true)
Playback rate range
The default playback rate range varies depending on the player engine. For the .apple player, the range is from -1.0 to 2.0. For the .castlabs player, the minimum rate is 0.0, and the maximum rate is undefined.
If you needed, you can use the API below to modify the range.
PRESTOplaySDK.shared.setPlaybackRateRange(of: .apple, to: 0.0...2.0)
PRESTOplaySDK.shared.setPlaybackRateRange(of: .castlabs, to: 0.0...2.0)
Video gravity
Video gravity determines how the video content is scaled or stretched within the player bounds.
The player layer supports the following video gravity values:
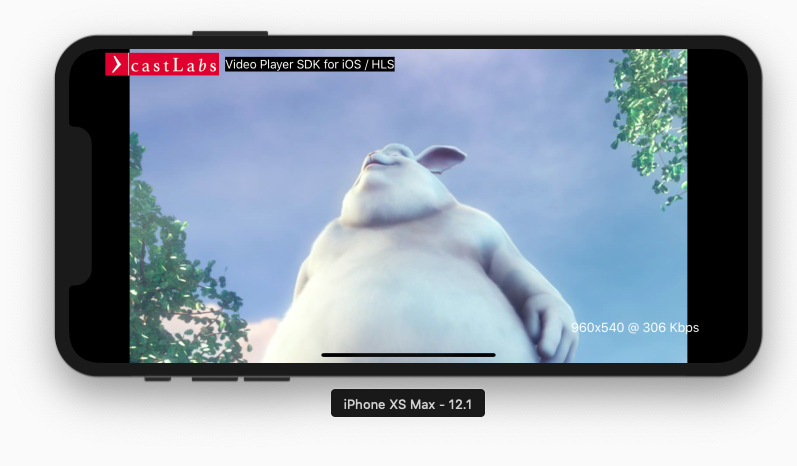
AVLayerVideoGravity.resizeAspectplayer should preserve the video’s aspect ratio and fit the video within the bounds,
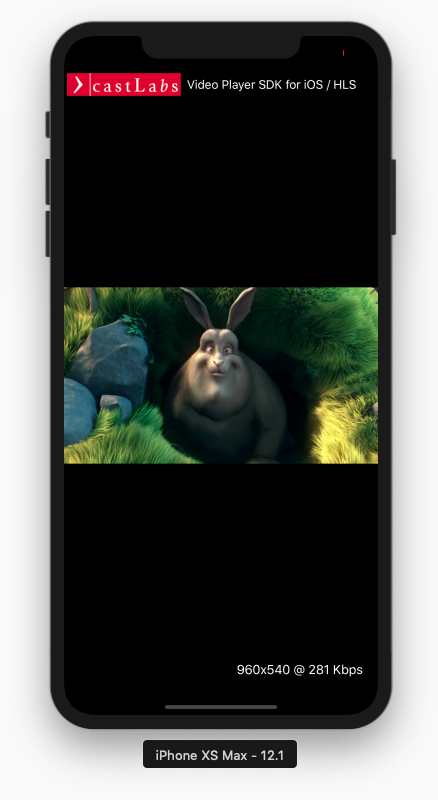
AVLayerVideoGravity.resizeAspectFillplayer should preserve the video’s aspect ratio and fill the bounds,
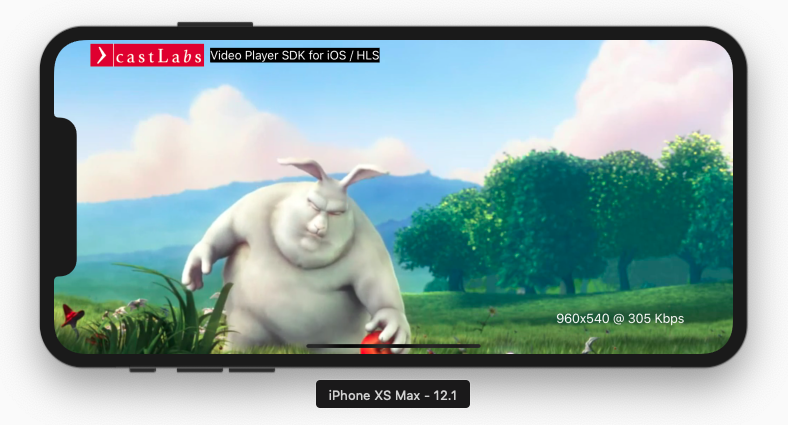

AVLayerVideoGravity.resizevideo should be stretched to fill the bounds

Phone call
By default the player is paused when a phone call has started and resumes playback when a phone call ends.
Player statistics
The Player API offers two main methods for accessing statistics data: onStats callback for real-time monitoring, ideal for logging QoE or other stats, and getStats method to fetch the latest stats programmatically. If stats aren’t available, nil is returned.
import PRESTOplay
import CastlabsApple
// Initialize the SDK and register the plugins
_ = PRESTOplaySDK.shared.setup("LICENSE", [HLSPlugin()])
// Create the player
var player = PRESTOplaySDK.shared.player()
guard let contentURL = URL(string: "https://example.com/master.m3u8")
else { return }
// Configure the player
let config = PlayerConfiguration(with: contentURL)
player.load(config: config)
// ...
// Observe stats
player.onStats = { stats in
print("Stats: \(stats)")
}
// Get the latest reported stats
let stats = player.getStats()
print("Stats: \(stats)")
// ...
Live Playback
Behind Live Window Warning
If the player’s position falls behind the live window, a non-fatal error (player_behind_live_window) is reported. AVPlayer will typically recover automatically.
The detection is based on the following condition:
position < max(0.0, seekWindow.start - tolerance)
The tolerance value compensates for timing drift between seekable time range updates and the player’s current position. By default the tolerance is set to 3 seconds. You can adjust the tolerance value using the following API:
// ...
let config = PlayerConfiguration(with: contentURL)
config.liveConfiguration = LiveConfiguration(behindLiveWindowTolerance: 5.0)
player.load(config: config)
// ...
Common Media Client Data (CMCD)
The SDK clients can transmit valuable information to Content Delivery Networks (CDNs) with each object request. Transmitting that data can improve QoS monitoring, adaptive traffic optimization, and delivery performance, ultimately enhancing the consumer experience. Specification - CTA-5004.
CMCD Support can only be enabled for adaptive streaming formats, DASH, HLS and SmoothStreaming.
CMCD Data Keys:
- CMCD-Request: keys whose values vary with each request.
- CMCD-Object: keys whose values vary with the object being requested.
- CMCD-Status: keys whose values don’t vary with every request or object.
- CMCD-Session: keys whose values are expected to be invariant over the life of the session.
CMCD Data is transmitted as HTTP Request headers.
To Enable CMCD, an instance of CmcdConfiguration needs to be created and passed to the PlayerConfiguration which is used for building the player.